Bulgaria
Bulgaria is a growing economy and the government has taken steps to present Bulgaria as an investor destination with 10% flat corporate tax rate, and a further reduction on corporate tax for investors that are investing in backward regions or regions that have high unemployment.
Need more information about payroll, compliance and social security in Bulgaria?
Talk to a specialist
Our free global insight guide to Bulgaria offers up-to-date information on international payroll, income tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and key updates on legislative changes and more in 2024.
Basic Facts about Bulgaria
Bulgaria is located in south eastern Europe and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, and by Greece and Turkey to the southwest and southeast. Bulgaria’s eastern coastline meets the Black Sea, offering trade links with the rest of Eastern Europe and the Near East.
A parliamentary republic, Bulgaria is an industrialised developing country, with a large private sector and an economy that has grown significantly since the early 2000s.
General Information
- Full Name: The Republic of Bulgaria
- Population: 6.465n (World Bank, 2022)
- Capital: Sofia
- Major Language: Bulgarian
- Major Religion: Christianity
- Monetary Unit: Lev
- GNI Per Capita: US $13,722 (World Bank 2022)
- Main Exports: Electrical machinery and equipment, mineral fuel, lubricants, transport equipment, food and live animals.
- International Dialling Code: +359
How Do I Say in Bulgarian?
- Hello: Здравей/Zdravei - if greeting one person
- Hello: Здравейте/Zdraveite - polite form, and if greeting more than 1 persons
- Good morning: Добро утро/Dobro utro
- Good evening: Добър вечер/Dobar vecher
- Do you speak English?: Говорите ли английски?/Govorite li angliiski?
- Good bye: Довиждане/Dovizhdane
- Thank you: Благодаря/Blagodaria or Мерси/Mersi
- See you later: До скоро/Do skoro
Dates & Numbers
Dates are usually written in the day, month and year sequence. For example, 1 July 2024 or 1/7/24.
Numbers are written with a period to denote thousands and a comma to denote fractions. For example, BGN 3.000,50 (three thousand and fifty BGN).
Doing Business in Bulgaria
Bulgaria stands out as an increasingly attractive destination for businesses looking to expand internationally.
The nation boasts a stable macroeconomic environment and a strategically beneficial location that provides seamless access to key markets—in Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
What sets Bulgaria apart is its commitment to maintaining financial stability, with the lev, its currency, tied to the euro under a currency board arrangement. This provides a significant level of financial predictability for businesses operating in diverse economic climates.
When you choose to operate in Bulgaria, expect a welcoming business climate. The country features competitive costs of doing business, especially labour costs, which are among the most favorable in the EU. Additionally, Bulgaria offers various incentives for entrepreneurs and investors, including a simplified tax regime and various operational benefits under the Investment Promotion Act. These incentives are tailored to encourage investment in sectors such as manufacturing, IT, and green energy.
Why Invest in Bulgaria
Investing in Bulgaria presents multifaceted opportunities backed by strong governmental support and a forward-thinking economic strategy.
The investment landscape in Bulgaria is designed to sustain growth and innovation. Bulgaria’s membership in the European Union brings with it a wealth of benefits, including access to a broad market and funding programs aimed at various sectors, with an emphasis on infrastructure, innovation and SMEs.
Capitalising on the well-established industrial sectors, such as machinery and electronics, Bulgaria is forging ahead to attract cutting-edge investments.
Investors are invited to explore the burgeoning sectors like software development and engineering services, which have been growing above the global average. Real estate investment, particularly in business, logistics, and retail sectors, continues to demonstrate robust growth trends providing attractive ROI potential.
Bulgaria is a growing economy and the government has taken steps to present Bulgaria as an investor friendly destination. As well as the 10% flat corporate tax rate, the government offers reduced corporate tax for investors that are investing in backward regions (less industrialised) or regions that have high unemployment.
Foreign Direct Investment in Bulgaria
Bulgaria represents a promising location for international business expansion, offering substantial opportunities to savvy investors.
Located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Bulgaria's strategic geographical position provides an ideal gateway for accessing key markets across continents.This, enhanced by the country's commitment to maintaining a favourable and equitable business environment with one of the lowest corporate tax rates in the EU, constitutes a robust foundation for global investors.
Bulgaria's labour market adds another layer of attractiveness to its FDI profile. The country hosts a highly skilled, affordable, and multilingual workforce, exceptionally proficient in technical fields and sectors such as IT, finance, and engineering. Hence, it’s a compelling destination for companies looking to develop their operations and scale up their talent pool.
In terms of regulatory considerations, Bulgaria has positioned itself as a neutral player, offering equitable rights to both local and foreign investors. Its inclusive approach extends to tax incentives and subsidies, designed to stimulate investment in areas struggling with high unemployment and to support the training of employees. This transparent and encouraging legal environment plays a crucial role in facilitating smooth and successful foreign investment.
Potential investors would do well to explore Bulgaria's rich variety of sectors presenting strong FDI opportunities:
- Manufacturing: High-end industries like automotive and pharmaceuticals offer sustainable investment growth possibilities.
- IT & Telecom: Rapid digital transformation across industries presents a ripe landscape for investment in leading-edge IT and telecom solutions.
- Real Estate: Despite the global economic context, the buoyant real estate sector continues to yield stable growth, sparking the interest of local and international investors.
- Green Energy: With Bulgaria's ongoing drive for sustainable development and renewable energy infrastructure, this sector opens a vibrant array of investment avenues.
As well as the 10% flat corporate tax rate, the government offers reduced corporate tax for investors that are investing in backward regions (less industrialised) or regions that have high unemployment.
Business Banking in Bulgaria
It is not mandatory to pay the authorities or employees from an in-country bank account, however, it is mandatory that they are paid from an account held by the employer.
Registering a Company and Establishing an Entity in Bulgaria
All companies in Bulgaria must have a legal entity before processing payroll.
Companies must be registered with the Trade Register at the Recording Agency. The Trade Registry Act allows a two-day term to complete the registration procedure, counted from the moment of filing the application for registration together with the respective documents at the Trade Register.
All employees and labor agreements must be registered with the Tax Office within 1 day of starting work.
Types of Business Entities in Bulgaria
There are several types of entities, the most common are:
Limited Liability Company (OOD)
This is the most common entity for small to medium-sized businesses. An OOD requires a minimum of one shareholder (individual or corporate) and one director, with no minimum capital requirements.
Joint Stock Company (AD)
Suited for larger businesses, an AD requires a board of directors and a minimum share capital of BGN 50,000, with 25% paid upon registration.
Branch Office
Foreign companies may establish a branch office. While not a separate legal entity, it operates as an extension of the parent company and must register with the Bulgarian Commercial Register.
Representative Office (RO)
Foreign businesses can set up an RO for non-commercial activities. It's mainly used for marketing or research purposes and must be registered with the Bulgarian Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
Registration Process
To register a business in Bulgaria the following steps are required:
Step 1: Trade Register Application
Begin by filing an application with the necessary documents at the Bulgarian Trade Register. The Trade Registry Act permits a two-day registration term upon the filing of your application.
Documentation Checklist:
- Company charter or memorandum and articles of association
- Proof of company name uniqueness
- Initial Board of Directors' minutes or decision demonstrating the intent to create the entity
- Declarations of consent and compliance from directors
- Evidence of capital deposit for AD entities
Step 2: Tax Office Registration
Once your company is registered, turn to employment considerations. Each employee and labor agreement requires registration with the local Tax Office within one business day of commencing work.
Step 3: VAT Registration
If your entity's turnover exceeds BGN 50,000 within any 12 month period, mandatory VAT registration is required. Businesses may also voluntarily register for VAT before reaching this threshold.
Step 4: Additional Registrations and Compliance Checks
- Obtain a Statistical Identification Number (BULSTAT) from the Registry Agency
- Register for social security and health insurance contributions
- Check industry-specific requirements for additional licenses or permits
Step 5: Data Protection Compliance
Ensure compliance with data protection regulations, which may include registering with the Commission for Personal Data Protection if your entity processes personal data beyond routine HR activities.
Visas and Work Permits in Bulgaria
Visas
There are 3 types of visa in Bulgaria, these are:
- Visa A – for airport transit
- Visa C – for a short stay, transit or planned stay
- Visa D – for a long stay
Visa applications forms are submitted no earlier than 3 months before the date of the intended travel, personally or through an authorized agent, with the exception of humanitarian cases.
Documents to be submitted with the visa application:
- A photocopy of the first page of the foreign travel document
- A photocopy of the last Bulgarian and Schengen visas or visas for the UK and the US, if any
- A colorful photograph 3,5 cm х 4,5 cm against light-colored background (the same holds for a child entered in the passport) – a full-face photo with clear, large enough face which takes up 70-80% of the photo; eyes must be red; the following is ineligible: photos with dark glasses; non-professional photos or cut out of amateur photos
- A medical insurance valid for the EU member states for the whole period of the trip, covering all costs for repatriation and for urgent medical care and emergency hospital treatment for the period of the stay indicated in the visa. The insurance amount cannot be less than €30,000.00
- Tickets (original and copy) or ticket booking conformation or financial means
- Copy of the technical passport of the car of the trip
- For under-aged children travelling without their parents or trustees the following documents shall be submitted:
- a copy of the birth certificate
- original and photocopy of a power of attorney notary certified by both parents/ trustees or by one parent trustee that they agree their child to travel unaccompanied by them.
The following persons are exempt from presenting proof for subsistence, accommodation and transportation:
- Members of the families or the households of European Union, European Economic Area and the Swiss Confederation citizens
- Persons applying for a visa for a long stay in view of gathering their families, in relation to a refugee status acquired or asylum in the Republic of Bulgaria – pursuant to a written decision of the State Agency for Refugees with the Council of Ministers
- Holders of service and diplomatic passports
Residence Permits
Foreigners who wish to reside in Bulgaria on a long-term basis (more than three months within each six-month period) should apply for and obtain a residence permit.
Family members of European citizens, who are not European citizens themselves, who wish to reside in Bulgaria for a period longer than three months, should be granted residence permits and should obtain residence cards.
Residence permits for Foreigners, the certificates for European citizens and the residence cards for European citizens’ family members who are not European citizens themselves, are issued by the Migration Directorate at the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
There are 3 types of residence permits available:
- Extended residence permit – with a term of validity of up to one year
- Long-term EU residence permit – for initial period of five years and option for renewal
- Permanent residence permit – for an indefinite period.
Once the Foreigner is granted an extended residence permit, they may live, reside and travel in Bulgaria while the permit is valid. The Foreigner may freely choose and change their place of residence, or leave the country and enter it again.
Foreigners who have obtained an extended residence permit have all the rights and obligations granted to or imposed on the Bulgarian citizens, with the exception of such rights and obligations for which Bulgarian citizenship is required. For example, Bulgarian employers can employ them, receive social security compensations, health care insurance, etc.
Residence Certificates
European citizens who intend to stay in Bulgaria longer than three months are issued residence certificates.
European citizens are issued two types of residence certificates:
- Long-term residence certificate – with a term of validity of up to five years
- Permanent residence certificate – for an indefinite period of time.
The grounds for issuance of long-term residence certificates are:
- The European citizen is employed or self-employed in the Republic of Bulgaria
- The European citizen has medical insurance and sufficient financial resources to cover the expenses for their residence and that of the family members without being a burden to the Bulgarian social security system, and
- The European citizen has enrolled in a school/college/university in Bulgaria for study, including professional training, and has medical insurance and sufficient financial resources to cover their expenses and that of the family members without being a burden to the Bulgarian social security system.
- In order to apply for a long-term residence certificate, the European citizen should submit an application to the Migration Directorate at the Ministry of Internal Affairs within three months after their first entry in the Republic of Bulgaria.
Income Tax in Bulgaria
The tax year in Bulgaria runs from the 1st January to 31st December each year.
Income Tax
Income tax is payable in Bulgaria, regardless of whether or not they are a local or foreign employee. Those who have a permanent residence in Bulgaria, spends more than 183 days in Bulgaria over 1 fiscal year from 1 January to 31 December, who resides abroad on assignment of the Bulgarian State and who has his/her center of vital interests in Bulgaria are liable to pay income tax.
Local natural employees have an obligation to pay taxes on income originating from sources located either within the Republic of Bulgaria or abroad. Foreign employees shall have an obligation to pay taxes on income originating from sources located within the Republic of Bulgaria.
There are tax reliefs in place (there will be a reduced tax rate). Examples include young families, income not exceeding the minimum salary and for persons with reduced capacity for work.
All income earned in Bulgaria is taxed at a flat rate of 10%.
Taxes must be submitted by the 25th date of the month for the previous month. Late submission can result in a penalty of €250.00 - €500.00 and interest on the amount owed.
Corporate Income Tax in Bulgaria
The entities liable to pay corporate tax in Bulgaria are:
- The local legal entities –trade companies
- The local legal entities that are not traders
- The local unincorporated entities and the insurance funds established
- The foreign legal entities that carry out economic activity in Bulgaria from a permanent establishment
- The foreign unincorporated entities that carry out economic activity in Bulgaria from a permanent establishment
Corporate tax is not paid by entities liable to alternative taxes. These are the enterprises funded by the budget, the organisers of the gambling games, and the entities engaged in ships’ operation activities.
The tax rate for corporate tax in Bulgaria is 10%.
The returns must be submitted and paid (if there are no advance returns) by 31st March of the next calendar year. The return must be submitted to the Office of National Revenue Agency (NRA) where the taxable entity is registered via post or the internet. The return is paid via the bank using a payment order, internet or postal order.
Advanced returns are applicable under the following circumstances:
- Monthly advance payments – they are made by taxable entities whose net sales income for the previous year exceeds BGN 3 000 000.
- Quarterly advance payments – are made by taxable entities that have no obligation to make monthly advance payments. Notably, these are the taxpayers whose net sales income for the previous year is in the range between BGN 300 000,01 and BGN 3 000 000 inclusively. Quarterly advance payments can be also made by taxpayers that are released from paying in advance.
The deadlines for advanced returns are as follows:
- Monthly advance payments: for January, February and March – paid by April 15th, and for the months from April to December – paid by the 15th day of the current month;
- Quarterly advance payments: for the first and second quarter - paid by 15th day of the month following the quarter, and for the third quarter – until December 15th. No quarterly advance payment is made for the fourth quarter.
Social Security in Bulgaria
Social security is applicable in Bulgaria.
It is a form of protection for employed persons in the case of loss of income.
The National Social Security Institute (NSSI) is the public institution that manages the state social security in Republic of Bulgaria.
Persons subject to state social insurance are insured in:
- "General (Non-occupational) Disease and Maternity" fund for common diseases and maternity, which includes insurance for temporary incapacity for work, temporary reduced working capacity and maternity
- "Pensions" fund for disability due to general (non-occupational) disease, old age and death
- "Labor Accidents and Occupational Diseases” fund for labor accidents and occupational diseases, which includes disability, death, temporary incapacity for work and temporary reduced working capacity due to labor accident or occupational disease
- "Unemployment" fund for unemployment
Contributions must be made by the 25th of the next month. The maximum social security income is BGN 3,750 (EUR 1,917) per month.
Social Security Contribution Rates
Employees born before January 1, 1960
|
Description - Employees born before January 1, 1960 |
Paid by Employer – 60% |
|
Social Security – PF |
13.12% |
|
Social Security – Fund labour accident and professional sickness paid by Employer for both type of employee |
0.40%-1,1% |
|
Social Security - Unemployment |
0.60% |
|
TOTAL |
14.12% - 14,82% |
|
Health Insurance - paid by Employer for both types of employee |
4.800% |
Employees born after December 31, 1959
|
Description - Employees born after December 31, 1959 |
Paid by employer – 60% |
|
Social Security – PF |
10.32% |
|
Social Security – Fund labour accident and professional sickness paid by Employer for both type of employee |
0.40%-1.1% |
|
Social Security - Unemployment |
0.60% |
|
Additional obligatory pension contributions paid by Employer only for Employee born after December 31,1959 |
2.80% |
|
TOTAL |
14.12% - 14,82% |
|
Health Insurance - paid by Employer for both types of employee |
4.80% |
Employees born before January 1, 1960
|
Description - Employees born before January 1, 1960 |
Paid by Employee – 40% |
|
Social Security – PF |
10.18% |
|
Social Security - Unemployment |
0.40% |
|
Social Security – Health |
3.20% |
|
TOTAL |
13.78% |
Employees born AFTER December 31, 1959
|
Description - Employees born AFTER December 31, 1959 |
Paid by Employee – 40% |
|
Social Security – PF |
7.98% |
|
Social Security – Additional obligatory pension contributions paid by Employer only for Employee born after December 31, 1959 |
2.20% |
|
Social Security - Unemployment |
0.40% |
|
Social Security - Health |
3.20% |
|
TOTAL |
13.78% |
Calculation Example
Gross Salary: 900 BGN
Social Security Base: 900 BGN
Contributions Employer: 170.28 BGN = 900*18.92%
Contributions Employee: 124.02 BGN = 900*13.78%
Tax: 77.60 BGN = (900-124.02) *10%
Net Salary: 698.38 BGN = (900-124.02-77.60)
Reporting Tax in Bulgaria
Monthly
There is a monthly submission of Declaration 1.
This is information for the social contributions of the employee. It is submitted electronically to Tax Office (NAP) and a Proxy can do this. The deadline is the 25th of the following month.
There is a monthly submission of Declaration 6.
This is information for the contributions which the employer is obliged to pay electronically to the Tax Office. Again, a Proxy can do this. The deadline is the 25th of the following month.
Yearly
There is a yearly submission of Information under Art. 73, para. 6 of the Personal Income Tax Act for the incomes paid during the year under labor legal relations. The deadline is the end of February of the following year.
When the employee has other incomes and they have an obligation to declare it to the authorities. The employee needs a certificate of income employment for the previous year. The certificates need to be issued by the employer.
New Employees in Bulgaria
Once the Labour Agreement has been finalised with the employee, there is a three-day term for the Agreement to be registered with the National Revenue Agency. Failure to register the Agreement can result in severe penalties for the employer.
Regardless of the three-day term, the agreement should be registered prior to the employee starting of work.
For example, if an agreement is concluded on January 3rd, 2021 and the employee is to start performing his/her functions under the agreement on this same date, the labour agreement must be registered with the National Revenue Agency first and only after that the employee may start legally to follow his/her obligations under the agreement.
Leavers in Bulgaria
When there is a leaver, there is a seven-day term to send notification for the termination to the National Revenue Agency.
Payroll in Bulgaria
It is legally acceptable to provide employees with online payslips in Bulgaria provided that they confirm that they received the payslip. Usually, payslips are provided on paper and the employee would sign the payslip.
Reports
Payroll reports must be kept for 50 years. If the company goes into liquidation, the payroll reports must be archived with the National Social Security Institute.
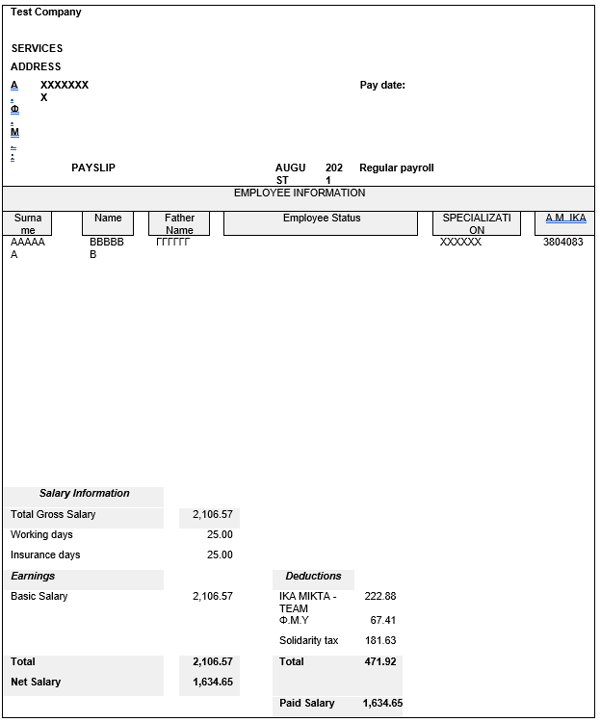
Bulgarian Payslip Example (English)
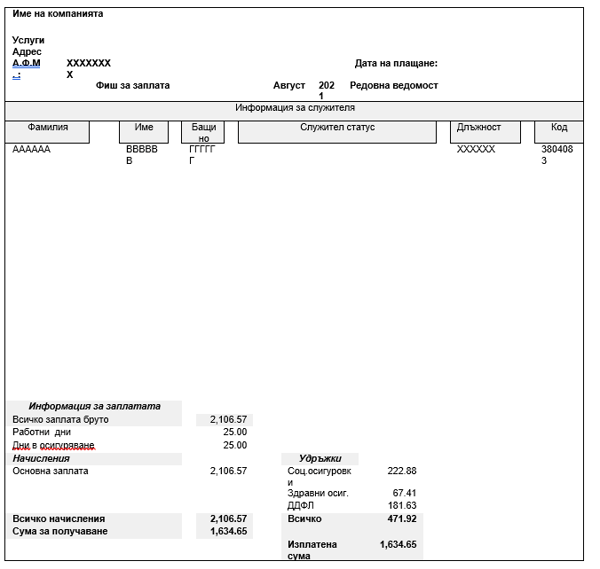
Bulgarian Payslip Example (Local Language - Bulgarian)
Employment Law in Bulgaria
Holiday Accrual and Calculations
Every employee is entitled to 20 days holiday once they have been in employment for 4 months (irrespective of the employer).
The employee can use their annual leave entitlement either in parts or all at once within the relevant calendar year.
Public holidays are not included in the calculation of annual paid leave.
Maternity Leave
Pregnant employees are entitled to 45 calendar days paid leave before delivery and a total of 135 days after delivery.
The maternity leave of 410 calendar days for each child (who is not sent for adoption or to a specialised institution of raising at the expense of the State) starts after 135 days pregnancy period.
After paid leave maternity for 410 calendar days, the mother is entitled to use additional paid leave until the child becomes two years old. This leave is paid from NSSI. The amount of this paid leave is determined annually according to the law on state social insurance. For 2024 it is 780 BGN.
Employees that are on maternity leave receive indemnity payments from the National Social Security Fund, if they have 12-months working experience recognized for social security purposes and have paid social security contributions covering this social security risk.
Maternity leave payments amount to 90% of the employee's average wage on which social security contributions have been calculated and paid for the period of 24 months preceding the maternity leave.
Paternity Leave
The father is entitled to paid leave of 15 calendar days after the discharge of the child from the hospital, if he has acquired 12 months' working experience.
The leave is paid by the National Social Security Institute in an amount determined in the same manner as applicable for indemnification for maternity leave.
Once the child has reached six months, the father can use the remaining maternity leave, with the mother's consent. In this case, the father is entitled to the same benefits as the mother if she had used her maternity leave.
Fathers (adoptive fathers) are entitled to 2 months leave for raising a child up to 8 years old.
The leave is paid by the National Social Security Institute in an amount determined in the same manner as applicable for indemnification for maternity leave. For 2024 it is 780 BGN.
Sickness
The employee must have been registered with Social Security for 6 months before claiming any sick leave.
The first 3 2 days of sick leave are paid by the employer at the rate of 70% of the gross salary. The Authorities pay the rest at a rate of 80% of the average daily gross salary. An average is taken from the last 18 months.
Calculation example
There is a total of 6 days sick leave.
The employee’s gross salary is 1000 BGN for the last 21 working days and the average gross salary for the last 18 months is 18500 BGN.
For the first 3 2 days the employee receives 1000/21*2*70%=66,67 BGN from Employer and for the remaining 4 days the employee is paid 18500/376*2*80%=78.72 BGN from the Authorities.
National Service
There is no National Service in Bulgaria.
National Minimum wage in Bulgaria in 2024
As of January 1, 2024, the national minimum wage in Bulgaria has been set at BGN 933 per month, which corresponds to approximately €477.
This adjustment represents not only a commitment to the economic stability but also to the social welfare of employees in the region.
For hourly waged employees, the minimum hourly rate has been set at BGN 5.58, translating to roughly €2.85.
Working Days and Working Hours in Bulgaria
The working week in Bulgaria is Monday to Friday, with the weekend usually being Saturday and Sunday.
In Bulgaria, Sunday is a mandatory day off.
Statutory National Holidays in Bulgaria 2024
There are multiple statutory holiday schedules within Bulgaria. Below are the statutory national holidays in Bulgaria for 2024.
|
Holiday |
Date |
Weekday |
|
New Year's Day |
1 January |
Monday |
|
Liberation Day |
3 March |
Sunday |
|
Bulgarian Liberation Day Holiday |
4 March |
Monday |
|
Labour Day |
1 May |
Wednesday |
|
Good Friday |
3 May |
Friday |
|
Holy Saturday |
4 May |
Saturday |
|
Easter Sunday |
5 May |
Sunday |
|
Easter Monday |
6 May |
Monday |
|
Culture and Literacy Day |
24 May |
Friday |
|
Unification Day |
6 September |
Friday |
|
Independence Day |
22 September |
Sunday |
|
Independence Day Holiday |
23 September |
Monday |
|
Christmas Eve |
24 December |
Tuesday |
|
Christmas Day |
25 December |
Wednesday |
|
Second Day of Christmas |
26 December |
Thursday |
Employee Benefits in Bulgaria
Expenses
In Bulgaria, employees receive 0.6% remuneration on their main salary for each year of professional experience. For example, an employee has 7 years’ experience and the main salary is 1000 BGN then the benefit would be 7 x 0.6% = 4.2% or 1000 x 4.2% = 42 BGN. This benefit is mandatory.
Some general expenses include:
- Food Vouchers for up to 200 BGN per employee
- Travelling from home to work with public transport is tax-free. Social Security must be paid on travel expenses. The expenses can be added to the employee’s salary however, it would be taxable and subject to social security contributions.
Expenses for company cars aren’t taxable, except when the car is used for management purposes (from manager) or for personal needs from managers and employees. If the company only pay for gasoline for the car mileage when car’s employee is used for official activities (not personally needs) then there is no integrated sum into a payroll.
Key updates for 2024 in Bulgaria
In Bulgaria, there have been several key regulation and legislation changes in 2024 affecting income tax, social security, and employment law:
Minimum Wage Increase
As of January 1, 2024, the minimum wage in Bulgaria has been increased from BGN 780 to BGN 933, which translates to a net pay of BGN 723.99 after deductions.
Retirement Age Adjustments
The retirement age and years of service required have been adjusted for various work categories and genders.
For instance, in the third category of work, women need 62 years and 2 months with 36 years and 6 months of social security experience, while men require 64 years and 7 months with 39 years and 6 months of experience.
Notes
Please note that this document gives general guidance only and should not be regarded as an authoritative or complete statement of the law, regulations or tax position in any country. You should always seek specific advice for each specific situation. This document should not be relied upon as professional advice and activpayroll accepts no liability for reliance on its contents.
Want to learn more about payroll, tax, social security and more?
Register free today to get the latest up-to-date information on international payroll, tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and more.
Let’s Partner
Talk to a specialist today and find out how we support the growth of over 500 businesses with a range of activpayroll solutions designed to help your global payroll and people operations succeed.
