China
With liberalisation measures stimulating growth and opening the country to investment, China has become the second-largest economy in the world: in 2022 its GDP stood at an estimated $18.1 trillion.
Need more information about payroll, compliance and social security in China?
Talk to a specialist
Our free Global Insight guides offer up-to-date information on international payroll, tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and more.
Basic Facts About China
China is one of the world’s largest sovereign territories - and its most populous.
It lies at the eastern edge of Asia, bordered by a number of the region’s most prominent nations including Russia, India and Pakistan, and sharing maritime borders with South Korea, Japan, Vietnam and the Philippines.
China’s earliest civilisations stretch back to prehistory, but the country was ruled by a series of grand imperial dynasties for centuries - until 1912, when the old system was replaced by the Republic of China.
In 1949, the Communist Party established the People’s Republic of China and, after a period of socialist rule, opened up to the world with economic reform in 1978.
China’s landscapes include mountain ranges, grasslands and plains, contrasting with densely populated urban centres like the capital, Beijing.
China’s climate shifts between dry seasons and monsoons, while temperatures vary greatly across every corner of the country thanks to a diverse topography.
General Information
- Full Name: People’s Republic of China
- Population: 1.412 billion (World Bank, 2022)
- Capital: Beijing
- Primary Language: Mandarin
- Main Religion: Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, Taoism
- Monetary Unit: Yuan
- Main Exports: Electrical machinery and equipment, furniture, cotton, tea and rice
- GNI Per Capita: US $12,850 (World Bank, 2022)
- Internet domain: .cn
- International Dialing Code: +86
How do I Say in Mandarin?
- Hello: 你好
- Good morning: 早安
- Good evening: 晚上好
- Do you speak English?: 你会讲英语吗?
- Good bye: 再见
- Thank you: 谢谢
- See you later: 回头见
Dates and numbers
Dates are usually written in the year, month and day sequence.
Example: 2020/07/08
Doing Business in China
Home to over 1.4 billion people, the People’s Republic of China is the most populous country in the world.
Once a Soviet-style planned economy, following 30 years of social and political reform, in the 21st century China has repositioned itself as a thriving market-economy.
With liberalisation measures stimulating growth and opening the country to investment, China has become the second-largest economy in the world: in 2019 its GDP stood at an estimated $14.14 trillion with a growth rate of 6.1% and a purchasing power parity of around $27.3 trillion.
Low labour costs have made China a leading global manufacturing location, while a huge domestic market and excellent access to the rest of Asia has encouraged international businesses to explore opportunities within the country.
China is an influential regional and global power and is a member of the G20, BRICS, APEC, and the WTO. In 2019, China was ranked the second largest recipient of foreign direct investment in the world after the United States, and was ranked 31 on the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business Survey.
Why Invest in China?
China’s economic reforms were designed to increase consumerism and serve a growing middle class, but foreign investment can still be a constantly changing process. Depending on the desired market, access can be easily achieved, or completely refused - and each case must be considered on an individual basis. That said, many of China’s industries are benefiting international business, including products from a range of manufacturing sectors, and the mining industry. Initiatives like the establishment of the Shanghai Free Trade Zone represent a bold step by the Chinese government to introduce new levels of FDI to the country.
Business Banking in China
It is mandatory to make payments to both employees and the authorities from an in-country bank account. In general, the opening hours for banks in China are 0900-1700. Banks are closed on Saturday and Sunday.
Registering a Company and Establishing an Entity in China
The company is required to have a legal entity established in order to process a payroll. They require an entity before they sign the labour contract with the employees.
Foreign employers can register the following entities in China:
Representative Office (RO)
Registration time is around two months.
Wholly Foreign Owned Enterprise (WFOE)
This is a form of limited liability company in China. The registration time is around three months.
Visas and Work Permits in China
Employment Visa (Z visa)
It is necessary for anyone who would like to work in China to obtain a China Visa. They must obtain a China Visa whether or not they bring their family with them. This China work permit must also be obtained if providing commercial entertainment in China. In both cases, it is necessary that the sponsoring employer meet the obligatory expectations.
To be issued with a China Visa, an individual must be considered a foreign expert/have a particular sought-after skill. The company sponsoring the employee must have a certificate to prove this.
The company sponsoring the employee will fulfil its side of the bargain to help the employee get a China Z Visa by giving the employee an employment permit (which is provided by the country’s government) as well as a visa notification letter that must be provided to the government (or Global Visas) along with photocopies of the China work visa application. Family members are also allowed to apply for a China Z Visa by showing a certificate indicating their relationship to the applicant, whether they are a wife, husband, or dependent.
The China Visa is only valid for one month or 30 days from when the employee arrives, after which it will expire. The employer must then apply for a Foreign Worker’s permit and a Residence Permit to replace the China Z Visa. Both of which are valid for one (1) year.
DSB
DSB is the sole organisation affiliated with China’s Foreign Ministry for those that work for foreign embassies and foreign media. Chinese citizens that are working with the foreign embassies and the foreign media must be registered with the DSB.
DSB issue working passes to foreigners and Chinese nationals working with foreign embassies/ media, no other company can issue the working passes. Currently, activpayroll nor its partner in China have a relationship with the DSB and as such, cannot support payroll activities related to foreign embassies/media in China.
Income Tax in China
The tax year runs from 1 January to 31 December.
Individual Income Tax (IIT): The employee has the duty for tax filing every month.
Each city/region has a Tax Bureau and Social Security Bureau that can be contacted for more information.
Monthly individual income tax is usually paid by the 15th of the following month except for special months due to public holidays, which the tax bureau will postpone the due date of the tax payment.
The penalty for late payment of individual income tax is 5/10000 of the amount owed per day.
Standard Deduction
Effective as of 1 October 2018, the standard deduction on comprehensive income is RMB 5,000 per month for both resident and non-resident taxpayers.
Monthly Tax Calculation
According to the new tax regulations effective from January 1 2019, the monthly individual income tax = cumulative tax payable – cumulative tax withheld in previous period.
[Cumulative tax payable = cumulative taxable income × withholding rate – quick deduction
Cumulative taxable income = cumulative income (excluding tax-exempt income) – cumulative applicable deductions (including personal deduction, special deductions, itemized deductions and other applicable deductions)]
Social Security in China
There are two mandatory statutory contributions, outlined below.
Social Security
China’s standard social security scheme comprises a system called the “Five Insurances” – the basic pension, medical insurance, work-related injury insurance, unemployment insurance and maternity insurance. Contribution to China’s social security system is mandatory for Chinese employees and their employers as well as foreigners employed in China. The social security contribution is calculated as a percentage of employees’ monthly salary, which is subject to lower and upper cap. The caps are adjusted every year.
Both employers and employees are required to make contributions (actual rates differ per city or province) to the following funds:
| Employee contribution | Employer contribution |
|
|
The employer or payroll agent needs to report to the local Social Security Bureau during the first week of the current month. If social security is paid late the government will calculate the amount owed (if any).
Housing Fund
Housing Fund contributions are mandatory for both the employee and the employer, except for foreigners. Contributions are made on a monthly basis.
Reporting Tax in China
Monthly Social Security Report
Information required for completion of this document is as follows:
- Monthly Social Security Registration
- Monthly Social Security Termination
- Contribution Information
The document can be filed by the employer or their authorised agent and must be submitted to the Local Social Security Bureau. The document is required to be signed by the employer.
Monthly Individual Income Tax Report
Information required for completion of this document is as follows:
- Monthly Individual Income Tax Summary
- Detail Information
The document can be filed by the Employer or their authorised agent and must be submitted to the Local Tax Bureau. The document is required to be signed by the employer.
New Employees in China
When a new employee starts, he/she must be registered with the Social Security Bureau. Registration will be done by the employer or agent before the 15th of the current month if hired before the 15th.
When setting up a new start, the following information is required:
- Employee information
- Monthly salary, start date
- Location of contributing social security and housing fund
When setting up an expat, the following additional information is required:
- Passport
- Work permit
Registration for an expat will be done by the employer or agent before the 15th of the current month if hired before the 15th.
Leavers In China
Payment for leavers will usually be made before the regular payment date. The authorities do not have to be notified of a leaver.
Payroll in China
Reports
Payroll reports must be kept for at least five years.
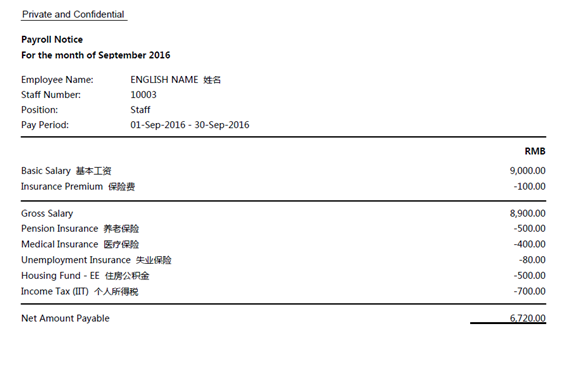
Payslip Example
It is legally acceptable in China to provide employees with online payslips.
Local language example:
Employment Law in China
Holiday accrual and calculations
The statutory annual leave entitlement is generally based on an employee’s work experience/ tenure. Employers may extend paid annual leave entitlement as an additional benefit to their employees.
Employees who have worked at a company for one continuous year are entitled to five days annual leave. Thus, employers do not have to give leave to employees who have not yet worked for one full year.
Statutory annual leave
| Work tenure | Days leave |
| Less than one year | 0 |
| 1-10 years | 5 |
| 10-20 years | 10 |
| Over 20 years | 15 |
It is important to note that the work tenure is not limited to the length of time an employee has worked for their current employer, but rather refers to their cumulative work experience with all previous and current employers.
Maternity leave
Maternity leave entitlement is up to 128 or 158 days after the birth, depending on province.
Paternity leave
Paternity policies vary vastly across China, especially when operating in a different province. Paternity leave length and pay is determined by location of employment, and can also be subjected to the company policy. There are no existing paternity leave policies for foreign workers in China; whether or not paternity leave can be taken is therefore at the discretion of the employer.
Sickness
Sick leave entitlement will depend on the following factors:
-
Total number years of the service
-
Years of working history in the current organisation
Working Days and Working Hours in China
The working week in China is Monday to Friday. General opening hours for commercial offices are 0900-1200 and 1300-1800.
Employee Benefits in China
Expenses
All expenses are tax deductible if official receipt (fapiao) is provided.
Notes
Please note that this document gives general guidance only and should not be regarded as an authoritative or complete statement of the law, regulations or tax position in any country. You should always seek specific advice for each specific situation. This document should not be relied upon as professional advice and activpayroll accepts no liability for reliance on its contents.
Want to learn more about payroll, tax, social security and more?
Register free today to get the latest up-to-date information on international payroll, tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and more.
Let’s Partner
Talk to a specialist today and find out how we support the growth of over 500 businesses with a range of activpayroll solutions designed to help your global payroll and people operations succeed.