Egypt
Egypt, as one of Africa's largest economies and a bridge between the Middle East and Africa, presents a dynamic environment for doing business. Egypt is a member-state of the UN, the Arab League, the African Union, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.With a strategic geographic location that includes the Suez Canal, a major global trade route, Egypt offers unparalleled access to markets in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Need more information about payroll, compliance and social security in Egypt?
Talk to a specialist
Our free global insight guide to Egypt offers up-to-date information on international payroll, income tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and key updates on legislative changes and more in 2024. Our guide to Egypt in 2024 is currently being updated and will be published soon.
Basic Facts about Egypt
Egypt is situated at the continental junction of Asia and Africa, and is a regional gateway between North Africa and the Middle East.
Civilization in the territory, which became Egypt stretches back to prehistory, and saw the rise of a prolific empire, and the creation of architectural wonders such as the Sphinx and the Pyramids.
Egypt was assimilated by various world powers over millennia - and was most recently ruled by Britain and the Ottoman Empire.
Gaining its independence in 1922, Egypt gradually became a regional power - although it is still considered to be a ‘middle power’ on the world stage.
Egypt’s climate is predominantly hot and dry, and much of the country is covered in desert terrain.
The location of a range of ancient landmarks, and stretches of beautiful coastline, Egypt has become an incredibly popular tourist destination for visitors from across Europe and the world.
General Information
- Full Name: Arab Republic of Egypt
- Population: 110.9 million (World Bank, 2022)
- Capital: Cairo
- Major Language: Arabic
- Major Religion: Islam (90%), Coptic Orthodox Christian (9%) and other denomination of Christianity (1%)
- Monetary Unit: Egyptian Pound (“Livres Egyptiennes”) 1 Egyptian Pound (EGP) = 100 piastres
- GNI Per Capita: US $4,100 (World Bank 2022)
- Main Exports: Crude Petroleum, Petroleum Gas, Refined Petroleum, Gold and Nitrogenous
- International Dialling Code: +20
How Do I Say in Arabic?
- Hello: مرحبا
- Good morning: صباح الخير
- Good evening: مساء الخير.
- Do you speak English?: هل تتحدث الإنجليزية؟
- Good bye: وداعا
- Thank you: شكرا
- See you later: اشوفك بعدين
Dates
Dates are usually written in the day, month and year sequence. For example, 1st July 2024 or 1/7/24.
Doing Business in Egypt
Egypt, as one of Africa's largest economies and a bridge between the Middle East and Africa, presents a dynamic environment for doing business. Egypt is a member-state of the UN, the Arab League, the African Union, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.With a strategic geographic location that includes the Suez Canal, a major global trade route, Egypt offers unparalleled access to markets in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
The country's government has been implementing reforms aimed at enhancing the investment climate, streamlining business operations, and encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI). Here's what you need to know about venturing into the Egyptian market.
Egypt's economy is diverse, with significant contributions from agriculture, industry, tourism, and services sectors. The government's ambitious economic reform program, initiated in 2016, has led to substantial improvements in fiscal stability and investment laws. These reforms, coupled with Egypt's large and young population, offer a promising consumer market and labor force for businesses across various sectors.
Egypt's strategic location not only serves as a pivotal gateway between continents but also hosts the Suez Canal, an essential link for international trade. The country has been investing heavily in infrastructure development, including new cities, industrial zones, and transportation networks, enhancing connectivity and access to local and international markets. This infrastructure development supports Egypt's vision to become a leading trade and logistics hub in the region.
Doing business in Egypt presents a compelling proposition for investors looking to tap into an emerging market with strategic significance, a large consumer base, and diverse investment opportunities. As Egypt continues to implement reforms and open its economy, the prospects for business and investment are increasingly promising. Companies willing to navigate the complexities of the Egyptian market can find fertile ground for growth and expansion in this historically rich and strategically located country.
Why Invest in Egypt?
Egypt, with its strategic geographical position and reform-oriented economic policies, has emerged as a beacon for investors eyeing the Middle East and Africa.
Situated at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe, Egypt's strategic location is unparalleled. The Suez Canal, one of the world's most important waterways, facilitates about 12% of global trade, offering investors a gateway to international markets. This prime geographic advantage is complemented by Egypt's access to key markets through various free trade agreements, making it a strategic hub for export-oriented businesses.
Situated at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe, Egypt's strategic location is unparalleled. The Suez Canal, one of the world's most important waterways, facilitates about 12% of global trade, offering investors a gateway to international markets. This prime geographic advantage is complemented by Egypt's access to key markets through various free trade agreements, making it a strategic hub for export-oriented businesses.
The Egyptian government has implemented significant reforms to improve the investment climate and attract FDI. Recent measures include modernizing investment laws, streamlining business registration processes, and enhancing the legal framework for investment. Additionally, Egypt offers a range of incentives for investors, including tax exemptions, customs duty reliefs, and investment zones offering special benefits.
Egypt's Vision 2030 aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), emphasising economic, social, and environmental sustainability. The government's commitment to sustainable practices offers opportunities for investments that contribute to green growth, social inclusion, and environmental preservation.
Investing in Egypt offers a unique blend of strategic advantages, from its pivotal location and large market potential to a favorable investment climate and diverse sectoral opportunities. For investors looking to capitalise on the growth dynamics of the Middle East and Africa, Egypt represents a promising frontier with a forward-looking approach to development and innovation. Whether it's leveraging the country's renewable energy potential, tapping into its rich consumer market, or participating in its ambitious infrastructure projects, Egypt stands ready to welcome and nurture global investment.
Foreign Direct Investment in Egypt
The nation's strategic geographical positioning as a bridge between Africa and the Middle East, combined with its burgeoning market and ambitious economic reforms, creates a fertile ground for international businesses looking to expand their horizons.
Egypt's government warmly welcomes FDI, recognising its pivotal role in advancing economic growth, technological advancement, and job creation. With sectors such as renewable energy, infrastructure, real estate, and information technology primed for growth, the stage is set for investments that not only yield significant returns but also contribute positively to the country's development trajectory. The Egyptian Investment Law of 2017, for instance, underscores this welcoming stance by offering incentives such as tax deductions and custom duties relief to foreign investors, a clear signal of Egypt's commitment to fostering a supportive business environment.
Foreign Direct Investment Opportunities in Egypt
Egypt's strategic location, young population, and diversified economy present numerous sectors ripe for FDI:
- Energy Sector: Leverage Egypt's vast solar and wind resources, especially in the Suez Canal Economic Zone.
- Manufacturing: Tap into various zones such as the Golden Triangle Economic Zone to engage in manufacturing, from textiles to electronics.
- Transportation: Projects aimed at modernising Egypt's transportation infrastructure, including port development and logistics services.
- Telecommunications and IT: Egypt's fast-growing ICT sector, supported by a well-educated, tech-savvy workforce.
- Healthcare: Invest in pharmaceuticals and medical devices, as Egypt boosts its health services.
- Banking and Financial Services: Opportunities for digital banking, insurance, and fintech.
- Tourism: Develop resorts, cultural experiences, and ecotourism in Egypt's rich historical tapestry.
Government Initiatives to Support FDI
To attract investors, Egypt has launched several initiatives:
- Investment Law No. 72 of 2017: Offers incentives, including tax breaks and customs duty waivers.
- Egypt 2030 Vision: A strategic plan fostering sustainable development, innovation, and international collaboration.
- Egypt's SME Support: Establishes avenues to finance and support SME growth.
- New Administrative Capital: Project to create a smart and sustainable city, envisaged to become a new economic hub.
- Industrial Licensing Reform: Simplifies the process for industrial projects, reducing start-up time and costs.
- Investor Services Centers: Provide investor-focused services for a streamlined start-up of operations.
- Decentralization Policy: Supports regional development, pushing growth outside of traditional economic centers.
In a climate of proactive enhancement of the investment environment, Egypt demonstrates its readiness to welcome international partnerships. Through a clear understanding of the global business landscape, and with precise knowledge of local requirements.
Business Banking in Egypt
To set up a business in Egypt and run payroll, a bank account is required.
Banking hours are 8.30am to 2:00pm (Sunday to Thursday) in the major towns and cities, with smaller towns and villages operating a more varied timetable.
Registering a Company and Establishing an Entity in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
A company is required to have a legal entity established in Egypt in order to process a payroll.
For integrating a company under the Investment Law in Egypt, the Investor has to conclude the endeavours of incorporation at GAFI (General Authority for Investment and Free Zones) to establish the company. The GAFI is a one-stop Business Services Centre. All business-related Egyptian Government agencies are now located under one roof. GAFI is empowered to negotiate and sign contracts, apply for licenses and approvals on behalf of all parties.
Foreigners may establish or acquire Egyptian companies.
Procedures for Establishing Companies in Egypt
The contract for establishing the company is submitted provided it follows the fields stipulated in Investment Law in Egypt.
The draft contract should enclose the following:
- Data form for the company, including purpose, capital, investment costs, and statement of partners, location, and expected labour
- Certificate determining the viability of company name, issued from the Commercial Register of Investment (at Ministry of Economy & Foreign Trade)
- A Bank Deposit Certificate with not less than 25% of the capital of joint-stock companies and 100% of the capital of companies with limited liabilities
The contract is assessed and authorised within 24 hours from the date of application. It is mandatory to legalize the signature of the lawyer who prepared the contract from the Bar Association in Cairo. After legalizing, it is submitted to the authority in order to issue a licensed decree with the establishment of the company within 24 hours from submitting the completed contract.
The applicant receives an official copy of the decree of the authority with the license to establish the company, enclosing an official copy of the contract and a letter to the competent commercial register office. The investor should provide the authority with a copy of the commercial register of the company after its registration.
Visas and Work Permits in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
In many countries, there is a separate work visa category. In Egypt, however, foreigners who intend to work just apply for a work permit. The application process for obtaining an Egyptian work permit has to go through a few stages and it may sometimes take a few months.
The application form can be collected from the nearest Ministry of Manpower and Training Office (in Cairo this is located within the Mugamma in Tahrir Square).
Other important documents required for making the application are as follows:
- A valid passport with valid Egyptian residence status
- 7 passport-size photos
- 2 copies of employer’s Incorporation Contract
- 2copies of tax ID
- 2 copies of academic
- A copy of the Commercial Register from your employer
- Any licenses required for practicing your profession
- A Memorandum from your employer explaining why it is necessary to hire a foreigner rather than a qualified Egyptian citizen
- Approval from the authority related to employee’s profession
- A representative from employer who will “sponsor” work permit
- Proof of test showing employee is free of HIV/Aids
- Approval from Egypt’s State Security Service showing that the employee is not a threat to national security or public safety
The registration fee is LE2500 to complete the process.
Income Tax in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
The Tax Year in Egypt is 1st January to 31st December.
It is the employer’s responsibility to file quarterly tax returns. The employer has one month after the end of each quarter to file the returns. Additionally, the employer is required to file annual salary tax reconciliation outlining salaries paid to each employee, deductions, exemptions, tax due, and the net salary paid to each employee.
The penalty of 1% per month is added for the late submission and payment of tax and social security contributions.
Residents and Non-Residents
All employers are required to calculate the salary and tax on the monthly basis which need to be remitted to the relevant tax offices within the first 15 days of the following month.
An employee on a Temporary Residence Permit or no citizenship status will be required to file a Tax Return on 1st January each year. Additionally, the employer is required to file a quarterly tax return. The employer has one month after the end of each quarter to file the quarterly tax returns.
At the Year-End, the employer is required to prepare an annual reconciliation of the salary tax to determine whether there are any disparities and to remit such tax disparities, if any, to the competent Tax Office within January of the following year.
Penalties are obligatory in the case of not complying with the due dates at 2% plus the discount rate declared by the Central Bank of Egypt. The discount rate is currently 11% (approximately).
Social Security in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
The Egyptian constitution specifies that the state must insure Social and Health Security Services and Retirement, Unemployment and Old Age Pensions for all citizens.
Employees benefit from the social security system in Egypt which provides insurance for all workers, whether they are subject to the Labour Law, state or public sector employees. The legislator did not make any distinction between workers in the government sector and workers in the non-government sector.
The social security system shall include the following:
- Old Age, Disability and Death Insurance
- Occupational Accidents Insurance
- Sickness Insurance
- Unemployment Insurance
- Social Care for Pensioners
The current Public Program in Egypt covers approximately 80% of employees, which is the highest among the developing nations. Contributions are based on two components:
- Floor amount for year 2021 is 1,200 Egyptian pounds a month
- Cap amount for year 2021 is 8,100 Egyptian pounds a month
Reporting Tax in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Monthly contributions should be made to the tax authority within 15 days of the following month.
Monthly contributions for social security payments should be made within 15 days of the following month.
Annual salary reconciliation, including the name of all employees, gross income, and tax calculation per year, has to be submitted before end of January of the following year
Key Legislative Authorities
- Investment Authority, Salah sales, Cairo.
- Tax authority, 5 Hussien Hegazy Street, Cairo.
- Social Insurance Authority, 5 Lazoghly Sq Monera, Cairo.
New Employees in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
In Egypt, the payroll and registrations of a new employee are the responsibility of the employer. All new employees have to be registered with the local authorities within 15 days of commencing employment.
Documents required for setting up a new start include:
- Employment Contract
- National ID
- Education Certificates
- Form (1) for Social Insurance
- Birth Certificate
- Valid Passport
- Work Permit
Leavers in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Payment for leavers is made in the employee’s last payslip. An employee’s final payment must be remunerated by the end of the month and social security must be notified of the termination of the employment contract.
Payroll in Egypt
It is acceptable to provide employees with online payslips.
Reports
Payroll reports must be kept for at least five years.
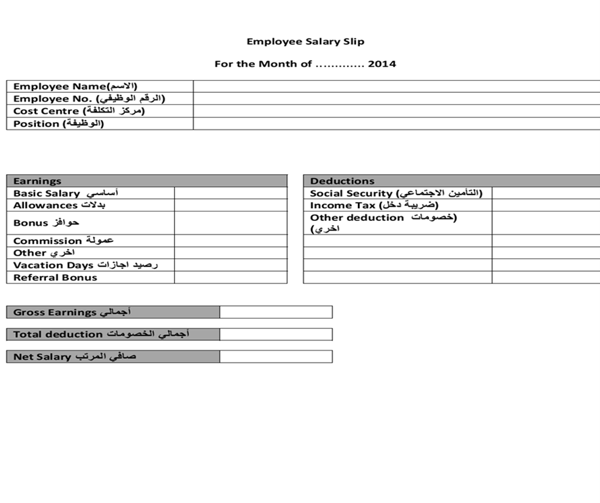
Egyptian Payslip Example
Employment Law in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Holiday Accrual and Calculations in Egypt
In accordance with the Labour Law, the amount of holiday allowance should be equivalent to 50% of the employee basic salary. The same applies to the Christmas allowance. The employer may grant the employee a percentage higher than the one quoted in the law.
Maternity Leave
A woman who has worked for 10 months for her employer is entitled to a maternity leave of 90 days with full salary.
Entitlement is up to 90 days after the birth. The salary is maintained and the employer pays 100% of the salary.
Paternity Leave
There is currently no paternity leave in Egypt.
Sickness
The Labour Law in Egypt proposes that an employee with an identified sickness by an approved medical professional is entitled to up to six months of paid sick leave annually, paid at the rate between 75% and 100% of the total wage.
National Service
In Egypt, military service is for males and all the wages are paid by the Egyptian Armed Forces during the military service.
National Minimum Wage in Egypt in 2024
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Working Days and Working Hours in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
A full workweek is generally considered as five eight-hour work days in Egypt, from Sunday through Thursday (to a maximum of six full days, which would generally add Saturday as the sixth).
National Statutory Holidays in Egypt in 2024
There are multiple statutory holiday schedules within Egypt. Below are the statutory national holidays in Egypt for 2024.
| Date | Weekday | Holiday Name |
|---|---|---|
| 7 January | Sunday | Coptic Christmas Day |
| 25 January | Thursday | January 25th Revolution and National Police Day |
| 10 April - 12 April | Wednesday - Friday | Eid Al-Fitr |
| 25 April | Thursday | Sinai Liberation Day |
| 1 May | Wednesday | Labor Day |
| 6 May | Monday | Sham El-Nessim |
| 16 June | Sunday | Arafat's Day |
| 17 June - 20 June | Monday - Thursday | Eid Al-Adha |
| 30 June | Sunday | June 30 Revolution |
| 8 July | Monday | Islamic New Year |
| 23 July | Tuesday | The July 23 Revolution Day |
| 16 September | Monday | Prophet Muhammad's Birthday (Mawlid Al-Nabi) |
| 6 October | Sunday | Armed Forces Day |
Employee Benefits in Egypt
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Expenses
In relation to general expenses, car mileage and company car expenses will only be included in the payroll if they are considered part of the employee’s income.
Each company must adhere to their individual expenses policy.
For example - car mileage is usually included in the payroll but each company holds their own specific reimbursement policy per mile.
Key updates in 2024 in Egypt
Corporate Tax
- E-Invoicing and Receipts Mandate: Taxpayers must submit electronic invoices or receipts for costs and expenses to be eligible for deduction. This requirement is effective for invoices from July 2023 and for receipts from January 2025.
- Electronic Invoices and Receipts: Deductibility of costs and expenses now requires supporting electronic invoices and receipts.
Personal Income Tax
- New Tax Brackets: The tax-exempt bracket is raised to EGP 30,000 annually, and a new tax rate of 27.5% is introduced for annual incomes exceeding EGP 1.2 million.
- Salary Tax Amendments: The personal exemption amount and the first bracket threshold subject to 0% tax have been increased.
These changes reflect a comprehensive overhaul in the Egyptian tax system, aimed at modernizing the tax regime and aligning it more closely with international standards.
Notes
Please note that this document gives general guidance only and should not be regarded as an authoritative or complete statement of the law, regulations or tax position in any country. You should always seek specific advice for each specific situation. This document should not be relied upon as professional advice and activpayroll accepts no liability for reliance on its contents.
Want to learn more about payroll, tax, social security and more?
Register free today to get the latest up-to-date information on international payroll, tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and more.
Let’s Partner
Talk to a specialist today and find out how we support the growth of over 500 businesses with a range of activpayroll solutions designed to help your global payroll and people operations succeed.
