Nigeria
Nigeria is diversifying its economy: agriculture, mining, manufacturing, real, estate, telecommunications, and financial services have all become important sectors while Nigeria itself has become one of Africa’s major banking markets, drawing a range of international investment interests.
Need more information about payroll, compliance and social security in Nigeria?
Talk to a specialist
Our free global insight guide to Nigeria offers up-to-date information on international payroll, income tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and key updates on legislative changes and more in 2024.
Basic Facts about Nigeria
Nigeria lies on the northwest coast of continental Africa, neighbouring Benin, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon.
Civilisation in Nigeria dates back to prehistory, but in the 18th and 19th centuries the country was colonised by European powers, and became part of the British Empire in the early 19th century.
In 1960, Nigeria declared its independence, and went through a period of political turmoil, including rule by military junta, until it emerged as a democratic nation in 1999.
Since its democratisation, Nigeria has emerged on the world stage as a member the Commonwealth of Nations and the United Nations, and a founding member of the African Union.
Thanks to its proximity to the equator, Nigeria is covered in lush, tropical rainforests and swamps, and by desert landscapes close to the Sahara region.
Nigeria’s climate varies between a wet season and a dry season but temperatures remain high throughout the year.
General Information
- Full Name: The Federal Republic of Nigeria
- Population: 218 million (World Bank 2022)
- Capital: Abuja
- Largest City: Lagos
- GNI Per Capita: US $2,140 (World Bank 2022)
- Main Industries: Oil & Gas, Agriculture, Mining, Manufacturing and Services
- Main Exports: Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Gas, Agriculture products, Minerals and Metals
- Main Language: English
- Monetary Unit: 1 Naira = 100 Kobo
- Internet Domain: .Ng
- International Dialling Code: +234
Dates
Dates are usually written in the date, month and year sequence. For example, 1 July 2024 or 1/7/24.
Numbers are written with a comma to denote thousands and a period to denote fractions. For example, N 5,000.20 (five thousand naira and twenty kobo).
Doing Business in Nigeria
Embarking on a business venture in Nigeria offers a landscape brimming with potential amidst its challenges. As the largest economy in Africa, Nigeria presents a dynamic market, with an expansive population and a diversified economic base that could mean robust opportunities for global businesses.
Nigeria’s economy is diverse, with key sectors including oil and gas, agriculture, telecommunications, and financial services. The country's size and resources have made it an attractive destination for foreign investment. Understanding sector-specific regulations and market entry strategies is crucial for businesses to flourish.
It is imperative for businesses entering Nigeria to familiarize themselves with the legal structure, which comprises a mix of English Common Law, Nigerian statutory law, and traditional law. The Nigerian Investment Promotion Commission Act and the Companies and Allied Matters Act are two critical pieces of legislation that govern foreign investments and corporate operations. The country's taxation system includes corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and withholding tax, among others, with specific considerations for the oil and gas sector.
Employing in Nigeria requires an understanding of the local labour laws, which cover everything from employment contracts to termination procedures. The country offers a large, young, and increasingly skilled workforce.
Nigeria is at the forefront of digital innovation in Africa. The growing tech sector, particularly in cities like Lagos and Abuja, showcases a burgeoning startup ecosystem. By tapping into this innovative spirit, businesses can leverage local talent and technology to drive growth.
Why Invest in Nigeria?
Nigeria, as Africa's most populous country and largest economy, offers expansive opportunities for businesses seeking to establish or grow their presence on the continent. Despite challenges familiar to emerging markets, Nigeria's potential benefits make it a compelling investment destination. Investing in Nigeria offers a gateway to exploring the untapped potential within the continent's most populous nation. Here are the main reasons why:
Substantial Market Size
Nigeria's population of over 200 million provides an exceptionally large market for goods and services. This translates to extensive customer bases for businesses across sectors, enabling high-capacity operations.
Diversified Economy
While Nigeria is known principally for its oil reserves, it has a remarkably diversified economy with key sectors including telecommunications, agriculture, manufacturing, and a growing digital economy. This diversity offers enterprises a broad field of opportunities to leverage.
Improving Business Environment
The Nigerian government is committed to making the country's business environment more investor-friendly. Enhanced legislative reforms, streamlined business registration processes, and improved access to credit are all indicative of this commitment.
Strategic Geographic Position
Nigeria's strategic position on the west coast of Africa provides a gateway to both the African continent and trans-Atlantic trade routes. This geographical advantage can be crucial for businesses involved in import/export or looking toward regional expansion.
Vibrant Labour Force
Nigeria's workforce is large, young, and increasingly well educated. This presents businesses with a valuable resource pool for recruitment and the opportunity to capitalize on local talent and creativity.
Partnering with Nigeria
Investing in Nigeria signifies a commitment to navigate its complex yet potentially rewarding business environment. As a progressive nation teeming with entrepreneurial spirit and investment opportunities, Nigeria offers an intriguing landscape for businesses ready to take the plunge.
Overall, investors are drawn to Nigeria's competitive advantages, including its large and youthful population, which fuels a growing consumer market, and its strategic position as a gateway to the African market. The Nigerian government supports foreign investment through incentives such as tax breaks, investment credits, and export promotion zones designed to reduce operational costs and enhance profitability. However, successful investment in Nigeria hinges on comprehensive market research, understanding local consumer behavior, and navigating regulatory requirements. Collaborating with local partners can also provide invaluable insights and access to networks that are crucial for navigating the business landscape effectively.
Foreign Direct Investment in Nigeria
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a pivotal role in Nigeria’s economic development, offering a pathway for international businesses to contribute to and benefit from Nigeria’s growth story. FDI in Nigeria spans various sectors, including oil and gas, manufacturing, telecommunications, and recently, tech-driven sectors such as fintech and e-commerce, reflecting the economy's evolving nature. The Nigerian government, keen on attracting FDI, has implemented policies to improve the business environment, such as enhancing legal frameworks, protecting investments, and simplifying the process of business establishment and operation.
The advantages of FDI in Nigeria include access to a large and growing market, the potential for high returns on investment given the country’s developmental stage, and the opportunity to tap into local resources, including a vast labor pool. Additionally, FDI contributes to technology transfer, skill development, and infrastructure improvement. For businesses considering FDI in Nigeria, it’s essential to assess sector-specific opportunities and challenges, understand the impact of regulatory changes, and engage with local stakeholders to ensure sustainable and mutually beneficial investments. FDI in Nigeria is not merely a transfer of funds, but a bridge of knowledge, skills, and technology, reinforcing the global partnership in business.The list of FDI opportunities is extensive, ranging from traditional sectors like oil and gas to emerging fields such as digital technology, renewable energy, and agribusiness, each offering unique prospects for growth and collaboration. Below is some of the FDI opportunities available:
-
Greenfield Investments: For businesses keen to start from the ground up, Nigeria offers plenty of opportunities for Greenfield investments, particularly in sectors such as technology, manufacturing, and agriculture.
-
Mergers and Acquisitions: For an expedited market entry, mergers and acquisitions are a viable choice, especially in established sectors, such as banking, insurance, and telecommunications.
-
Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances: Given the complex business environment, many foreign businesses prefer to partner with Nigerian companies to mitigate risk and leverage local know-how. This is particularly common in the oil and gas sector.
Nigeria's Vibrant Sectors for FDI:
-
Oil and Gas Sector: Despite efforts at economic diversification, oil and gas remain Nigeria's primary source of income and major attractor of FDI.
-
Agriculture Sector: With vast arable land, Nigeria’s agriculture sector holds significant growth potential for investments in agro-processing enterprises.
-
Telecommunications Sector: With one of the largest telecommunications markets in Africa, investments in this sector offer promising returns.
-
Manufacturing Sector: Nigeria's manufacturing sector, particularly in areas of fast-moving consumer goods, is continually growing and attracting foreign investment.
-
Digital Economy: Nigeria's burgeoning tech scene presents lucrative investment opportunities, particularly within the thriving fintech sector.
Registering a Company and Establishing an Entity in Nigeria
When planning to start a business in Nigeria, the first essential step is to register your business with the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC), the government agency responsible for regulating businesses in the country. The process can be complex and time-consuming, but with the right information and assistance, it's manageable.
Steps to Business Registration in Nigeria
- Determine the Business Name: Decide on a name for your business. Unique and distinct, it should not infringe on any existing trademarks or copyrights
- Conduct a Name Search: Conduct a search with CAC to ensure the proposed name is available
- Reserve the Proposed Name: If the name is available, you can reserve it for a period with the CAC
- Complete the Registration Process: Upon approval of the name, fill in the required details and complete the registration process
As you proceed with registration, you should consider which type of business entity to establish. The company is required to have a legal entity established in order to process a payroll. There are various types of entity available including:
- Private or Public Limited Liability Company (most common)
- Unlimited Liability Company
- Company Limited by Guarantee
- Foreign Company (branch or subsidiary of a foreign company)
- Partnership/Firm
- Sole Proprietorship
- Incorporated Trustees
- Representative Office
Visa and Work Permits in Nigeria
To work in Nigeria, all business visitors must obtain a visa. The application should be made prior to travelling to Nigeria. Applicants should make their request for visa to the Nigerian embassy within their country of origin or current residence. A visa may not be required by citizens of countries that have specific arrangements with Nigeria.
There are three main types of visa:
- Ordinary Visa
- Diplomatic Visa
- Gratis Courtesy Visa
The Ordinary Visa is further divided as follows:
- Transit
- Single Journey
- Multiple Journeys
Ordinary Visa
Transit
This type of visa is issued to applicants who wish to pass through Nigeria to a further destination. It may be obtained at a Nigerian mission and is given for a period not exceeding seven days without reference to the Comptroller-General of Immigration. A transit visa may also be given at the port of entry on the specific approval of the Comptroller-General of Immigration.
Single Journey
This is valid for a single entry into Nigeria and may be issued as:
- Short Visit Visa
- STR Visa (Subject To Regularisation for Residence Work Permit)
- W.P (Temporary Work Permit)
The Short Visit Visa
This type of single journey visa is issued to applicants who require a single entry to Nigeria for the purpose of tourism, and/or relations resident in Nigeria.
STR Visa (Subject to Regularisation)
This is the type of visa required by foreigners seeking to take up employment in Nigeria (for a period of more than 6 months).
The employer applies to the Nigerian embassy in the country of residence.
The STR Visa is issued at Nigerian mission without reference to the Comptroller-General of Immigration provided that the applicant presents specified documents. STR visa is normally given for 90 days
Regularisation of Stay
On arrival in Nigeria the expatriate is allowed a 3 month period from the date of his/her arrival to have his/her Stay in Nigeria regularised and his/her status upgraded to that of a Resident.
The Regularization process takes 7 to 10 working days to conclude. At the end of this time, the expatriate is issued a Temporary Residence permit. The more permanent Residence Permit (plastic green card) is issued within 3 months of issuance of the initial Temporary residence permit.
Note: Presently, Nigeria Residence permits are granted for a period of one or two years at the expiration of which the permit has to be renewed if the expatriate is to continue living/working in Nigeria.
Temporary Work Permit (T.W.P)
Companies wishing to engage the services of expatriates for short period assignments (2 – 6 months) are required to apply direct to the Comptroller-General in Abuja.This approval comes in the form of a TWP cable for such expatriates. On receipt of the approval, a foreigner wishing to visit Nigeria on TWP may make an application for a TWP visa at a Nigeria Mission in his country of residence.
The temporary assignments, which are eligible for such approval, include:
- Erection/Installation Work
- Feasibility Studies
- Repairs Of Machinery/Equipment
- Auditing Of Accounts
- Research Work
This Visa is given for a period not exceeding 2 months and may be extended for a further period.
Visa-On-Arrival (VOA)
The VOA is a short visit stay which is issued to business men on arrival at a Nigeria port. To obtain it, an application will have to be made locally to the Comptroller-General of the Nigeria Immigration Service for an approval. Thereafter, the approval is forwarded to the foreigner to enable him to board a plane to Nigeria and for presentation at the Immigration desk at a Nigeria entry port.
With a VOA approval, the foreigner has no need to visit a Nigeria Mission.
Gratis Courtesy Visa
This type of visa is normally issued to persons who do not qualify for diplomatic visa, but who are foreign government officials traveling on official business. It may be granted in cases where it is considered undesirable to accede to an application for a diplomatic visa, but where it is desirable on grounds of international courtesy to facilitate a journey.
Business Banking in Nigeria
It is mandatory to have an in-country bank account in Nigeria to process payroll.
Generally, banks are open to the public from 0800 to 1600 and are closed on Saturdays and Sundays.
Income Tax in Nigeria
The Tax Year runs from 1st January to 31st December.
All companies are required to register with tax authorities and obtain TIN (Taxpayer Identification Numbers). The registration process takes two to three weeks to be completed.
The contributions payable in respect of each month shall fall on the last day of the month concerned.
You must register with the following statutory authorities:
- Registration with Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS)
- Registration with Lagos State Internal Revenue Service (LIRS) – Provided operations will predominantly be in Lagos State.
- Registration with National Pension Commission (PenCom)
- Registration with Nigeria Social Insurance Trust Fund (NSITF)
- Registration with National Housing Fund (NHF)
- Registration with Industrial Trading Fund (ITF) - (the Minimum threshold for an employer to become liable under this scheme is when the employer has in its employ a minimum of 5 employees and/or if its annual turnover is in the region of N50 million.)
Note that some of these processes can overlap, i.e; they can be processed concurrently, excluding registrations with FIRS and LIRS where the former is a prerequisite for the latter.
Please note that some of these registrations may attract statutory fees that are not expressly stated.
Income Tax
Individuals resident in Nigeria are taxable on their worldwide income.
In the case of employment, a non-resident person is liable to tax in Nigeria if the duties of employment are wholly or partly performed in Nigeria, unless:
- the duties are performed on behalf of an employer who is in a country other than Nigeria,
- the remuneration of the employee is not borne by a fixed base of the employer in Nigeria, and
- the remuneration of the employee is liable to tax in that other country under the provisions of the avoidance of double taxation treaty (DTT) with that other country.
Personal income tax rates for 2024
The table below shows a summary of the taxable income tax bands and applicable rates of tax on an annual basis.
|
Monthly Gross Income - Naira |
Rate % |
Tax (Naira) |
Cumulative Tax |
|
First =N= 300,000 |
7% |
21,000 |
21,000 |
|
Next =N=300,000 |
11% |
33,000 |
54,000 |
|
Next =N=500,000 |
15% |
75,000 |
129,000 |
|
Next =N=500,000 |
19% |
95,000 |
224,000 |
|
Next =N=1,600,000 |
21% |
336,000 |
560,000 |
|
Above 3,200,000 |
24% |
768,000 |
1,328,000 |
Social Security in Nigeria
Social security contributions in Nigeria cover benefits for retirement, disability, sickness and maternity. Employees contribute a minimum of 8% of their salary, while employers must contribute around 10% to the various benefit schemes.
Reliefs and Allowances (Social Security)
Reliefs and Allowances in Nigeria are Tax Exempt Deductions available to individual taxpayer under the Personal Income Tax Act Cap P8 LFN 2004 (as amended) to lighten his tax burden. In addition to the reliefs and allowances, Personal Income Tax (Amendment) Act, 2004 as amended:
- Consolidated Relief Allowance (CRA) CRA is granted at the higher of ₦200,000 or 1% of gross income plus 20% of gross income. Gross Emolument means wages, salaries, allowances (including benefits in kind), gratuities, superannuation and any other income derived solely by reason of employment. Gross Income means “all incomes from whatever source derived, unless excluded by law
- Life Assurance Premium paid by the individual during the year preceding the year of assessment to an insurance company in respect of insurance on his life or the life of his spouse, or for a contract for a deferred annuity on his own life or the life of his spouse;
- National Pension Scheme. The Pension Reform Act 2004 establishes a uniform contributory pension scheme for payment of retirement benefits of employees. The scheme applies to all employees in both the public sector and private sector who are in employment in an organisation in which there are 5 or more employees.
Employers are required to contribute a minimum of 10% of their employees’ monthly emolument and employees are to contribute a minimum of 8%.
Reporting Tax in Nigeria
Based on Section 81 of PITAM, in Nigeria employers are required to file the Employers Annual Declaration (Form H1) return of all emoluments paid in the preceding year to its employees not later than 31 January of every year.
The return also includes the evidence of tax remitted by the employees and a projection of emoluments to be paid in the current year. Where an employer has in its employment an expatriate, the employer should include the relevant information of such expatriate(s) when filing the Form H1 returns.
New Employees in Nigeria
New employee are required to register with respective State internal revenue of the state in which they are resident. The process varies from one state to another. While some are automated or may be manual.
Below is an overview of the key areas required:
-
Obtain Necessary Employee Information:
Before you embark on the registration process, gather all necessary information from your new employee. This includes personal details, qualifications, and banking information. Such precision ensures the accuracy and compliance of your payroll operations from the outset. -
Register for Employer's Tax Identification Number (TIN):
If this is your first employment within Nigeria, your business must be registered with the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS) to obtain an Employer's Tax Identification Number (TIN). This is a prerequisite for remitting taxes and complying with local tax laws. -
Register with the National Pension Commission (PenCom):
In Nigeria, enrolling your employees in a pension scheme is a legal requirement. Register your company and your employees with a Pension Fund Administrator (PFA) of their choice and contribute to their retirement savings account as mandated by the Pension Reform Act1. -
Register for Employee Health Insurance:
The National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) is a critical component in providing your employees with necessary health benefits. Register your employees to ensure they have access to comprehensive health care services, promoting a healthy workforce. -
Register with the Nigeria Social Insurance Trust Fund (NSITF):
This step is about ensuring that your employees are covered by the Employee's Compensation Scheme, which provides comprehensive coverage in case of work-related accidents or injuries. -
Inform the Relevant Local and State Authorities:
Depending on your location and industry, there may be additional local or state regulations and bodies to inform about your new hire. It's advisable to research and comply with any regional requirements to ensure full legal compliance.
Leavers in Nigeria
In Nigeria, once an employee leaves the employment of a company, the tax authority must be advised accordingly.
Payroll in Nigeria
It is legally acceptable in Nigeria to provide employees with online payslips.
Reports
Payroll reports must be kept for a statuary period of six years.
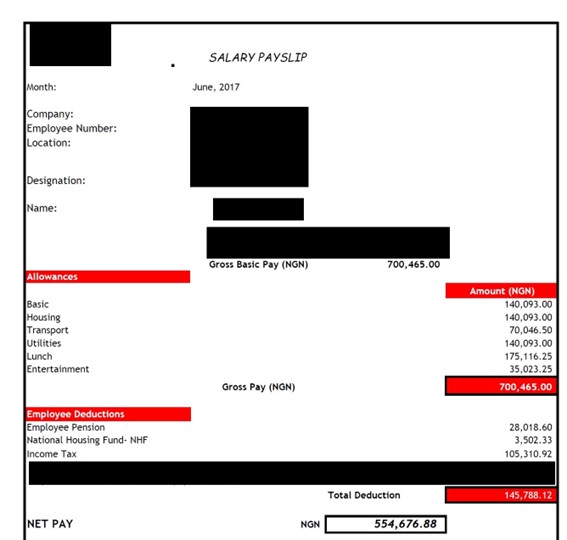
Nigerian Payslip Example
Employment Law in Nigeria
Holiday Accrual and Calculations in Nigeria
Nigerian Employment Laws requires that every employee in Nigeria, who has been in the employment of an employer for a continuous period of twelve months, is entitled to a holiday with full pay of at least six working days pay.
Leave pay is often calculated based on the worker's gross monthly wage and allowances. The gross monthly wage is divided by the total working days in a month to obtain the daily wage. This daily wage is then multiplied by the number of leave days to obtain the total holiday pay.
When calculating leave allowances, only the portion of a worker's earnings received in cash (excluding overtime and other allowances) should be considered for leave pay and health allowances.
It's essential to note that the specific policies and calculations may differ depending on the employer and any collective bargaining agreements in place.
Maternity Leave
In Nigeria, maternity leave policies are primarily governed by the Labour Act. In accordance with the Labour Act, maternity leave in Nigeria is split into:
- Pre-natal Maternity Leave: A female employee is entitled to a period of six weeks maternity leave prior to her confinement (delivery of the baby)
- Post-natal Maternity Leave: Following the birth, she's entitled to another six weeks - making up a total of twelve weeks.
In addition to the maternity leave duration, an extension of up to two weeks is possible on medical grounds.
During this maternity leave period, the employee is entitled to receive full pay if she has been employed for at least six months before the date of her expected confinement. While on leave, her position is protected and she cannot be terminated due to her absence.
Paternity Leave
There is no Paternity Leave Entitlement in Nigeria. However, companies can provide such benefits at their discretion or based organsational policy.
Sickness
Subject to the Workmen's Compensation Act, a worker shall be entitled to be paid wages up to twelve working days in any one calendar year during absence from work caused by temporary illness certified by a registered medical practitioner:
In the calculation of sickness benefits only that part of his wages which a worker receives in money (excluding overtime and other allowances) shall be taken into account.
National Service
The National Service was set up by the Nigerian government to involve the country’s graduates in the development of the country.
The body responsible for paying NYSC Corpers is primarily the Federal Government of Nigeria. The government, through the NYSC scheme, ensures that all Corps members receive a monthly allowance, commonly referred to as “allawee,” from the beginning to the end of their service year. This payment is regarded as a basic sustenance allowance and is meant to aid Corpers in covering basic needs.
However, it’s worth noting that in some cases, Corpers are paid additional stipends by the state governments or the private/public organisations where they are posted.
Working Days and Working Hours in Nigeria
The working week in Nigeria is Monday to Friday.
The working day for commercial offices is usually eight hours, typically from 0800 to 1700.
Lunch breaks range from half an hour to one hour.
Statutory National Holidays in Nigeria 2024
There are multiple statutory holiday schedules within Nigeria. Below are the statutory national holidays in Nigeria for 2024.
|
Name |
Day |
Date |
|
New Year's Day |
Monday |
1 January |
|
Good Friday |
Friday |
29 March |
|
Easter Monday |
Monday |
1 April |
|
Workers' Day |
Wednesday |
1 May |
|
Democracy Day |
Wednesday |
12 June |
|
Eid al-Fitr |
TBD |
TBD April/May |
|
Eid al-Adha |
TBD |
TBD June/July |
|
Independence Day |
Tuesday |
1 October |
|
Christmas Day |
Wednesday |
25 December |
|
Boxing Day |
Thursday |
26 December |
Please note that the dates for Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are to be determined (TBD) as they depend on the Islamic lunar calendar and the sighting of the moon, so the exact days will vary.
National Minimum Wage in Nigeria in 2024
The national minimum wage in Nigeria for 2024 is N35,000 per month based on a full time employee
Employee Benefits in Nigeria
Expenses
Amounts allowed are now limited to expenses incurred in performance of duties and from which it is not intended that the employee should make any gain or profit.
Employers must consider what qualifies as expenses incurred in performing employment duties as distinct from activities which are the personal responsibilities of the employee.
Cost of passage, medical reimbursement etc. may no longer qualify.
Key updates in 2024
In 2024, Nigeria's key updates in the areas of income tax, social security, and employment law are:
- Premiums paid by individuals to insurance companies for insurance or deferred annuity contracts on their lives or the life of their spouse become tax-deductible. However, any withdrawals made within 5 years will be subject to tax.
Notes
Please note that this document gives general guidance only and should not be regarded as an authoritative or complete statement of the law, regulations or tax position in any country. You should always seek specific advice for each specific situation. This document should not be relied upon as professional advice and activpayroll accepts no liability for reliance on its contents.
Want to learn more about payroll, tax, social security and more?
Register free today to get the latest up-to-date information on international payroll, tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and more.
Let’s Partner
Talk to a specialist today and find out how we support the growth of over 500 businesses with a range of activpayroll solutions designed to help your global payroll and people operations succeed.
