Thailand
With the manufacturing, tourism and energy industries growing in importance over the 20th century, Thailand’s economy is diversifying, and the country now boasts one of the lowest unemployment rates in Asia.
Need more information about payroll, compliance and social security in Thailand?
Talk to a specialist
Our free global insight guide to Thailand offers up-to-date information on international payroll, income tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and key updates on legislative changes and more in 2024. Our guide to Thailand 2024 is currently being updated and will be published soon.
Basic Facts about Thailand
Thailand lies at the centre of Southeast Asia and is bordered by Myanmar to the northwest, Laos and Cambodia to the east, and Malaysia to the south.
Thailand and its neighbours make up a large part of the Indochinese Peninsula, while its southern coast looks out onto the Gulf of Thailand - which provided historic maritime trade access and connections to the rest of the world.
Formerly known as Siam, Thailand’s earliest civilisations date back to prehistory and show visible religious and cultural influences from across Asia. Once ruled by an imperial dynasty, Thailand is now a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government and separate legislative branch.
Thailand’s tropical climate and scenic beauty is known across the world, and attracts millions of tourists each year: a variety of regional environments include thick forests, mountainous highlands and stretches of picturesque coastline - along with numerous island destinations. Temperatures and weather vary dramatically in Thailand - from hot, tourist friendly seasons, to warm, wet monsoons.
General Information
- Full Name: Kingdom of Thailand
- Population: 71.6 million (World Bank, 2022)
- Capital: Bangkok
- Primary Language: Thai
- Main Religion: Buddhism
- Monetary Unit: 1 baht = 100 satang
- Main Exports: Machinery including computers, vehicles, rubber, plastics, meat/seafood
- GNI per Capita: US $17,230 (World Bank, 2022)
- Internet Domain: .th
- International Dialing Code: +66
How Do I Say in Thai?
- Hello: สวัสดี / sà-wàt-dee
- Good morning: ดีตอนเช้า / sà-wàt-dee kráp (male), sà-wàt-dee kâ (female)
- Good evening: สวัสดี / sà-wàt-dee kráp (male), sà-wàt-dee kâ (female)
- Do you speak English?: คุณพูดภาษาอังกฤษได้ไหม / pôot ang-grìt dâai măi
- Good bye: ลาก่อน / sà-wàt-dee kráp (male), sà-wàt-dee kâ (female)
- Thank you: ขอขอบคุณคุณ / kòp kun mâak
- See you later: ไว้พบกันใหม่ / láir-o jer gun ná
Dates and Numbers
Dates are usually written in the day, month and year sequence. For example: 1 July 2019 or 1/7/19.
Numbers are written with a comma to denote thousands and a full stop to denote fractions, for example, 2,000.50 BHT (2000 baht and 50 satang).
Doing Business in Thailand
One of the largest nations in Southeast Asia, Thailand is part of the Indochinese Peninsula, and lies between Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Malaysia.
Although considered an emerging economy, Thailand is the second largest in Asia (behind Indonesia), with a GDP of around $543 billion.
As a newly-industrialised country, Thailand is heavily export-focused: exported goods and services make up two-thirds of the country’s GDP, amount to $105 billion of revenue each year, and include electrical and computer components, cars and automotive parts, agricultural products, and textiles.
With the manufacturing, tourism and energy industries growing in importance over the 20th century, Thailand’s economy is diversifying, and the country now boasts one of the lowest unemployment rates in Asia.
Why Invest in Thailand?
The Thai government welcomes inward investment from foreign investors to help develop the economy. Some incentives are available to encourage investors to support emerging industries within Thailand.
Business Banking in Thailand
It is not mandatory to make employee salary payments from an in-country bank account, however it is mandatory to make third party authority payments from an in-country bank account.
Registering a Company and Establishing an Entity in Thailand
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
The company is required to have a legal entity established in order to process a payroll.
The timescale for completion of this process is one - two months.
Typically, foreign investors will do business in the form of a limited company, branch or representative office. There are different regulations and different tax issues for each form. The most common choice is a limited company.
Limited Company
Formation of a limited company is regulated by the Civil and Commercial Code. There must be at least three persons to form a company; they must subscribe their names to a memorandum of association (MOA) and then register. Upon receiving the amount of shares, the director must register the company within three months from the date of company’s meeting to establish the company.
If more than 49% of the shares in the limited company are owned by non-Thai nationals, then the company is subject to the Foreign Business Act and the restrictions that it imposes.
Branch Office
In Thai law, the branch and its head office are a single legal entity. This means that the head office is liable for lawsuits brought against its branch in Thailand. The head office will be required to pay tax on transactions in Thailand, even when the Thai branch is not involved.
Representative Office
This form of company can only partake in limited business activities. This office is forbidden from rendering services for anyone other than its head office. It can only receive funds from its head office.
Treaty of Amity
The Treaty of Amity is a treaty between the US and Thailand which creates favourable trade conditions. The treaty allows citizens of the US to establish a business in Thailand with majority ownership, this is usually prohibited under the Foreign Business Act – usually the majority owner must be Thai national(s). A company can register under the Treaty of Amity if at least 51% of the company shares are owned by US citizens. Usually the directors of the company have to be US citizens. It should be noted that this exception for US citizens does not extend to all types of business activity.
Visas & Work Permits
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
To apply for a work permit the employee must first obtain a non-immigrant visa for themselves and all family members before traveling to Thailand. This visa usually allows for a stay of 90 days but can be extended up to a year. This visa can then be renewed each year.
There are several rules covering work permits in the Foreign Employment Act.
In the majority of cases all non-Thai nationals working in Thailand are required to have a work permit. The employer can file for a work permit before the employee is in Thailand, however they will not obtain it until they are in Thailand.
A new work permit is required if there is a change in certain job details – such as change in occupation, employer or location.
For urgent work an employee may be allowed to work up to 15 days without a work permit, however this work may only be done once written notification has been received from the Department of Employment.
Income Tax in Thailand
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Individual Income Tax (Taxes on Employment Income)
The tax year runs from 1 January to 31 December.
For employment income, a withholding system is in operation, whereby the employer deducts income tax from the employee’s salary or wage before paying it. Employers are responsible for submitting a monthly withholding tax return to the Revenue Department by the 7th day of following the month. The tax due must be paid at the time of filing the return.
Tax is calculated under the assumption that the payments of employment income are made throughout the entire length of the year. The annual amount of tax is calculated at the progressive tax rates prevailing. This tax is then divided by the number of payments; the result shall be the tax to be deducted.
Rate of tax
| Income (THB) | Tax rates % |
| 1 - 150,000 | 0 |
| 150,001 - 300,000 | 5 |
| 300,001 - 500,000 | 10 |
| 500,001 - 750,000 | 15 |
| 750,001 - 1,000,000 | 20 |
| 1,000,001 - 2,000,000 | 25 |
| 2,000,001 - 5,000,000 | 30 |
| 5,000,0001+ | 35 |
The penalty for late submission of WHT is as follows:
- 100 baht within first 7 days
- 200 baht from day 8 onwards
- An additional penalty of 1.5% of due amount added. This is calculated monthly – the penalty will never exceed the actual tax due on that occasion.
Social Security in Thailand
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
There are two mandatory statutory contributions:
Social Security Fund (SSF)
Both the employee and employer have to contribute on a monthly basis. The contribution rate is usually 5% with basic salary caped at THB15,000.00. With the minimum wage being increased recently, it has been decided to extend the reduction in Social Security contribution rate.
Monthly social security payments must be submitted by the 15th of the following month to the Social Security Department (www.sso.go.th). For instance, contributions for October must be paid by November 15th, after which they will be charged an extra 2% of the overdue amount each month until the payment is made.
Provident fund / Welfare Fund
Employers have the option of registering for a “provident fund” (offered by Thai financial institutions) instead of participating in the government’s “employee welfare fund” (overseen by the Department of Labour Protection and Welfare).
Depending on the fund’s prospectus, employees may contribute between 2% and 15% of their salary, and the employer matches this amount. Under the new rules, no matter what amount their employer is contributing, employees can contribute and deduct the maximum amount allowable—15% of annual wages or THB 500,000, whichever is lower. An employee can make higher contributions than the employer. Employee contributions are tax-exempt up to a certain limit, which means that yearly contributions up to that sum directly reduce the tax liability.
The payment for the provident fund must be submitted three days after payday and may vary depending on PF trustee.
Workmen Compensation (WCF)
In addition to social security contributions, the Workmen’s Compensation Act requires employers to pay annual contribution, at the rates of 0.2% - 1% of its employees’ annual wage depending on risk levels of the business. This contribution is to be used for paying workmen’s compensation in respect of work-related injury, or sickness, or loss of organs, or invalidity, or death, or lost to employees who are insured persons.
The annual wage per person for calculating the contribution amount is limited to Baht 240,000 per employee per year. The term “wages” means money of all kinds paid by an employer to an employee in return for work performed on a normal working day excluding overtime pay, holiday pay and bonus pay.
Reporting Tax in Thailand
Monthly
Employers are responsible for submitting Monthly Withholding Tax (WHT) on a monthly basis. The deadline is by 7th (manual submission) or 15th (online submission) of the following month. The amount can be calculated using the tax table supplied by the government.
Provident Fund (monthly)
The format of this is determined by the vendor.
Yearly
|
Description of Year End Element
|
Submission Date to Authorities
|
|
Form 26 Workmen’s Compensation Fund submission |
28th February every year |
|
Form of Kor Thor 20 A Workmen’s Compensation Fund submission |
28th February every year |
|
PND.1 K Form Tax form if the company had withheld the tax for acquisition of salary of the staff |
28th February every year |
|
PND 91 Taxpayer receiving income from employment during the period January to December, must pay personal income tax before the last day of March every year |
31st March every year |
New Employees in Thailand
It is required for all new starts to be registered with the following departments within the first month of employment:
- Provident Fund registration is required with the appointed Provident Fund vendor.
- SS registration required with the Social Security Fund.
- Revenue Department (this is not required if the new starter is a citizen of Thailand. If the new starter is an expat and never had TAXID then the company should apply TAXID for the expat employee)
Registration is usually submitted together with monthly PF and SS forms.
To set up a new start the following information is required:
- PF – New hire form containing all the personal & employment information
- SS – Standardized New hire form (Form SPS1-03/1)
The following documents are also required when setting up a new start:
- Passport
- Signed contract
- Work permit
- Working visa
- Personal I.D. Card (Thai staff)
- Tax ID card (expatriates only)
- Social Security Fund ID number (expatriates only)
Leavers in Thailand
All leavers must notify the local authorities if they are leaving their job by completing the following:
- PF – Termination form containing all the personal & employment information
- SS – Standardized termination form (Form SPS6-09)
Payroll in Thailand
In Thailand it is legally acceptable in Thailand to provide employees with payslips in either hard copy or online. Payslips are in English or Thai depending on the requirements of the company.
Reports
Payroll reports must be kept for at least seven years.
Thai Payslip Example
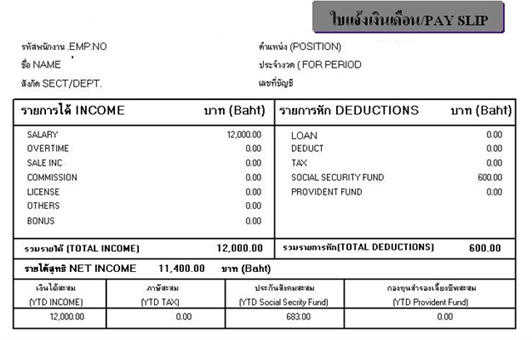
Employment Law in Thailand
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Annual Leave
Under the Labor Protection Act (LPA), an employee who has worked continuously for one full year shall be entitled to annual leave of not less than six working days.
In the interests of the computation of leave, when the employee is paid a monthly wage
Monthly Wage * No. of days of annual leave 30.
Maternity Leave
In Thailand, an expecting mother is protected under the Labour Protection Act. Women employees are entitled to the following:
- 98 days of maternity leave including any holidays in that period
- Full pay: 45 days from the employer and 45 days from the Social Welfare Fund
- Protection from termination of employment due to pregnancy
Note: To be entitled to paid maternity leave, the woman must have paid contributions to the Social Welfare Fund for at least seven months before pregnancy.
For further information, see the http://www.sso.go.th
Paternity Leave
Men are not entitled to Paternity leave. The announcement is not treated as law to which every employer must comply, so the announcement leaves the decision with employers to set the terms of the paternity leave and whether or not salary is paid during paternity leave.
Sick Leave
It is standard in Thailand to receive up to 30 days with pay. There are no particular calculation formulas for sickness payments.
National Service
As per the Labor Protection Act, an employee shall be entitled to take leave for military service for mobilization for inspection, for military training or for mass testing in accordance with the law on military service.
An employer shall pay a wage to an employee who takes leave for the purpose of military service under Section 35 equal to the wage on a working day throughout the entire leave period, but the number of such leave days must not exceed sixty days in a year.
Personal Business Leave
Employee must be given a minimum of 3 days business leave a year and full pay for a maximum of 3 working days a year while on business leave.
Note: Personal business leave is different from annual leave and must be addressed separately in the work rules. The Labour Protection Act stipulates 3 days of paid personal business leave.
National Minimum Wage in Thailand 2024
Thailand's approach to minimum wage is distinctive, ensuring that wage rates are reflective of the economic conditions across its diverse provinces. This stratification acknowledges the varying costs of living and economic activities from one region to another, aiming to balance employee welfare with economic sustainability.
The minimum wage in Thailand by Province for 2024 are:
| No. | Minimum Wage (Baht/Day) | Number of Provinces | Provinces |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 330 | 3 | Narathiwat, Pattani, Yala |
| 2 | 338 | 4 | Trang, Nan, Phayao, Phrae |
| 3 | 340 | 16 | Ranong, Satun, Loei, Nong Bua Lamphu, Udon Thani, Maha Sarakham, Sisaket, Amnat Charoen, Mae Hong Son, Lampang, Sukhothai, Uttaradit, Kamphaeng Phet, Phichit, Uthai Thani, Ratchaburi |
| 4 | 341 | 5 | Chainat, Sing Buri, Phatthalung, Chaiyaphum, Ang Thong |
| 5 | 342 | 5 | Nakhon Si Thammarat, Bueng Kan, Kalasin, Roi Et, Phetchabun |
| 6 | 343 | 3 | Yasothon, Lamphun, Nakhon Sawan |
| 7 | 344 | 3 | Phetchaburi, Chumphon, Surin |
| 8 | 345 | 15 | Kanchanaburi, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Surat Thani, Songkhla, Phang Nga, Chanthaburi, Sa Kaeo, Nakhon Phanom, Mukdahan, Sakon Nakhon, Buriram, Ubon Ratchathani, Chiang Rai, Tak, Phitsanulok |
| 9 | 347 | 2 | Krabi, Trat |
| 10 | 348 | 3 | Suphanburi, Nakhon Nayok, Nong Khai |
| 11 | 349 | 1 | Lop Buri |
| 12 | 350 | 6 | Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Saraburi, Chachoengsao, Prachinburi, Khon Kaen, Chiang Mai |
| 13 | 351 | 1 | Samut Songkhram |
| 14 | 352 | 1 | Nakhon Ratchasima |
| 15 | 361 | 2 | Chonburi, Rayong |
| 16 | 363 | 6 | Bangkok, Nakhon Pathom, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon |
| 17 | 370 | 1 | Phuket |
National Public Holidays in Thailand in 2024
There are multiple statutory holiday in Thailand. Below are the statutory national holidays in Thailand for 2024.
| Date | Weekday | Name of Holiday |
|---|---|---|
| 01 January | Monday | New Year's Day |
| 06 February | Tuesday | Makha Bucha Day |
| 06 April | Saturday | Chakri Memorial Day |
| 13 April | Saturday | Songkran Festival |
| 14 April | Sunday | Songkran Festival |
| 15 April | Monday | Songkran Festival |
| 01 May | Wednesday | Labour Day |
| 18 May | Saturday | Visakha Bucha Day |
| 28 July | Sunday | King Vajiralongkorn's Birthday |
| 12 August | Monday | The Queen Mother's Birthday |
| 13 October | Sunday | King Bhumibol Memorial Day |
| 23 October | Wednesday | Chulalongkorn Day |
| 05 December | Thursday | King Bhumibol's Birthday |
| 10 December | Tuesday | Constitution Day |
| 31 December | Tuesday | New Year's Eve |
Working Days and Working Hours in Thailand
The working week in Thailand is Monday to Friday.
Generally, the working hours for commercial offices are from 0830 to 1730.
Employee Benefits In Thailand
This information is currently being updated for 2024.
Expenses
Travel expenses can be reimbursed through payroll or other ways; there are no specific rules.
Notes
Please note that this document gives general guidance only and should not be regarded as an authoritative or complete statement of the law, regulations or tax position in any country. You should always seek specific advice for each specific situation. This document should not be relied upon as professional advice and activpayroll accepts no liability for reliance on its contents.

Key Updates for 2024 in Thailand
The Ministry of Labour announced an extension for the electronic payment deadline of Social Security contributions for the period of January through December 2024. This extension, detailed in a notification published in the Royal Gazette on 28 December 2023, grants employers an additional seven business days beyond the regular deadline for these payments. The table below outlines the adjusted deadlines for each month:
| Period | Regular Deadline | Extended Electronic Payment Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| January 2024 | 15 February 2024 | 27 February 2024 |
| February 2024 | 15 March 2024 | 26 March 2024 |
| March 2024 | 15 April 2024 | 25 April 2024 |
| April 2024 | 15 May 2024 | 27 May 2024 |
| May 2024 | 15 June 2024 | 25 June 2024 |
| June 2024 | 15 July 2024 | 25 July 2024 |
| July 2024 | 15 August 2024 | 26 August 2024 |
| August 2024 | 15 September 2024 | 24 September 2024 |
| September 2024 | 15 October 2024 | 25 October 2024 |
| October 2024 | 15 November 2024 | 26 November 2024 |
| November 2024 | 15 December 2024 | 24 December 2024 |
| December 2024 | 15 January 2025 | 24 January 2025 |
This adjustment aims to facilitate the process of making Social Security contributions electronically, ensuring that employers have adequate time to comply with their obligations.
Want to learn more about payroll, tax, social security and more?
Register free today to get the latest up-to-date information on international payroll, tax, social security, employment law, employee benefits, visas, work permits and more.
Let’s Partner
Talk to a specialist today and find out how we support the growth of over 500 businesses with a range of activpayroll solutions designed to help your global payroll and people operations succeed.